NVIDIA 100B investment in OpenAI - Implications for the AI Ecosystem
- Gianluca Luke Caccamo

- Oct 1, 2025
- 7 min read
Updated: Oct 2, 2025
Nvidia’s announced $100 billion investment in OpenAI is a landmark deal in the AI/infrastructure world — it carries far-reaching implications across competition, technology, regulation, and society as a whole. Let's dig dive into the specific of the deal and the overall implications for the ecosystem (jump straight to the interactive AI Strategic Alliances & Competitive Landscape map).
Breakdown of the deal between NVIDIA-OpenAI
First, some of the known facts and terms of the deal:
Nvidia will invest up to US$100B in OpenAI under a strategic partnership.
The deal involves building at least 10 gigawatts (GW) of Nvidia-powered AI data centers for OpenAI, with the first GW expected in H2 2026. For context, 10 gigawatts is about the same output as ten typical nuclear reactors, since a single reactor usually generates around 1 GW. Running at full capacity, that's roughly enough electricity to power 8 to 9 million US households for a year.
The investment is staged — payments/transfers will be made progressively as infrastructure (e.g. data centers) is deployed.
Nvidia gains a non-controlling equity stake in OpenAI.

Implications
The OpenAI–NVIDIA deal could redefine how AI is built, scaled, and monetized. These are the key implications — from the doors it opens to the challenges it creates.
Strengthening Nvidia’s Position
Locked-in customer & demand: By taking equity and committing large sums tied to hardware deployment, Nvidia essentially secures one of its biggest customers — OpenAI — for many years. This provides visibility into demand, helps in planning chip production, supply chain, etc.
Vertical integration: The deal nudges toward tighter integration of hardware (Nvidia) + software / models (OpenAI). This co-optimization can yield better performance, lower inefficiency, but also creates dependencies.
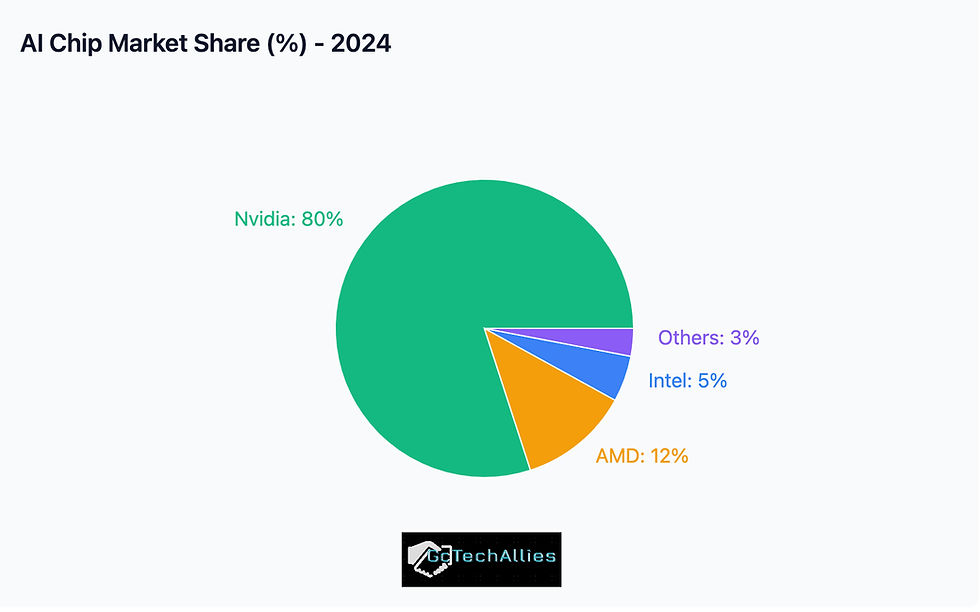
Barrier for competitors: Other makers of chips (AMD, Intel, custom silicon) may be at a disadvantage. OpenAI likely will have preferred access to Nvidia’s latest hardware, possibly first rights, better pricing, etc. That can widen the lead Nvidia has in the AI hardware market.
OpenAI’s Capabilities & Strategic Autonomy
Compute scale: Opening up 10 GW of compute gives OpenAI enormous scale. That enables training and deploying much larger, more capable models. It helps for both research (pushing frontiers) and operational usage (serving more users, with more features).
Reduced dependence on other infrastructure providers: OpenAI historically relied heavily on Microsoft (Azure) and other cloud providers. This deal gives more control and possibly improves negotiating power/supply certainty.
Regulatory / Antitrust / Competition Concerns
Antitrust scrutiny: Because Nvidia already has a strong position in the AI-chip / GPU market, the deal may draw regulatory attention. There are concerns that Nvidia could favor OpenAI in access, price, deliveries, etc., hurting other AI firms.
Market dominance concentration: Capital, compute, data, model research — all of these require huge investment. This kind of deal tends to concentrate power in fewer hands which might reduce competition, slow diversity in the ecosystem.
Technical / Operational / Infrastructure Risks
Power & Energy: Deploying 10 GW of data centers means massive energy needs: power generation, cooling, environmental impact. Finding grid capacity, managing electricity costs, environmental regulation will matter.
Permits, real estate, cooling infrastructure, etc.: Building big data centers is not only about getting chips; site selection, water cooling, local infrastructure, regulatory approval can slow things down. The deal is staged, so delays in any phase could delay investment or deployment.
Dependency risks: OpenAI becomes more tightly tied to Nvidia’s hardware roadmap. If Nvidia faces supply constraints, delays, or shifts its priorities/hardware design in inconsistent ways, OpenAI may suffer. Also risk if alternative hardware architectures become better — OpenAI might be exposed.

Societal, Ethical & Policy Implications
Acceleration of AI capabilities: Bigger models, more compute, faster iteration means potentially faster progress toward more advanced AI. Could lead to breakthroughs (positive), but also increases risk (e.g. misuse, safety, alignment issues).
Environmental impact: Energy consumption, carbon footprint—there is concern that AI compute is very power‐hungry. Scaling to many gigawatts has environmental consequences.
Access & inequality: Smaller players (startups, research labs in less wealthy countries) may find access to leading hardware harder; competition may favour incumbents. This can widen technological inequality.

Longer-run Implications
AGI / Frontier Models: To the extent OpenAI’s ambition includes developing more powerful, possibly “artificial general intelligence”-type systems, this investment gives it more of the compute and infrastructure runway required. Bigger models + more data + better hardware = faster progress.
Ecosystem shaping: Nvidia’s hardware architecture (chips, interconnects, software stack) may more deeply shape the design of future AI models (since OpenAI will likely optimize for what Nvidia hardware does well). Over time, this can reduce hardware diversity.
Competitive backlash or alternative development: Other big tech and governments may respond with similar scale investments, or push for alternative hardware ecosystems, open source designs, or regulation to ensure competition and prevent dependency.

Anticipating the Next Moves: How Other Players Might React and Realign
If Nvidia and OpenAI are tying themselves together with a strategic data center partnership, it forces everyone else in the ecosystem to rethink their moves. Below we compile a breakdown of likely reactions and counter-strategies from major players:
1. Big Tech Cloud Providers
Microsoft
Deepens ties with OpenAI (already a major investor + Azure backbone). Could feel squeezed if Nvidia takes a central role in compute.
Likely reaction:
Push for long-term exclusive AI hosting agreements with OpenAI to keep workloads on Azure.
Double down on AI infrastructure independence (custom silicon, e.g. Azure Maia AI chips).
Expand partnerships with Anthropic, Inflection, Mistral, or new labs to hedge risk.

Amazon (AWS)
Already pushing Trainium and Inferentia chips to reduce dependence on Nvidia.
Likely reaction:
Aggressive incentives for labs to build on Trainium 2 / Inferentia 3 instead of Nvidia GPUs.
Possible strategic stake in Anthropic or Cohere, to counterbalance OpenAI-Nvidia.
Position itself as the energy-efficient AI cloud — using renewables to contrast with Nvidia’s massive energy appetite.
Google (Alphabet)
Has TPUs and DeepMind/Google DeepMind models (Gemini).
Likely reaction:
Double down on Gemini + TPU vertical integration.
Extend licensing/partnership deals with other labs/startups that want to avoid the Nvidia-OpenAI orbit.
Potential government lobbying in EU/US on antitrust grounds.
2. AI Model Companies
Anthropic
Funded by Amazon and Google; focused on “safety-first” positioning.
Likely reaction:
Position itself as the credible OpenAI alternative for enterprises.
Accelerate multi-cloud strategy (AWS + Google) to avoid single-vendor lock-in.
Possibly align with AMD or a challenger to Nvidia to differentiate.
Cohere, Mistral, Inflection
Smaller but nimble.
Likely reaction:
Seek partnerships with alternative chipmakers (AMD, Intel, Cerebras, Graphcore) to secure preferential pricing and hardware access.
Join forces in lobbying for open standards and interoperability.
Explore strategic alliances in Europe or Middle East (sovereign compute initiatives).
3. Chipmakers / Hardware Providers
AMD
Biggest rival to Nvidia in GPUs.
Likely reaction:
Position as the “open partner” for labs that don’t want Nvidia lock-in.
Partner with Anthropic, Mistral, Cohere, Hugging Face to create a counter-ecosystem.
Increase collaboration with sovereign AI initiatives in Europe, India, Middle East.
Intel
Pushing Gaudi AI accelerators.
Likely reaction:
Partner with AWS or Anthropic to showcase large-scale deployments.
Play the “cost-effective alternative” card, especially for enterprises.
Specialized startups (Cerebras, Graphcore, SambaNova)
May benefit from labs seeking diversity of compute.
Likely reaction:
Align with governments / research universities for public AI infrastructure projects.
Focus on niche workloads (ultra-large model training, HPC).
4. Governments & Sovereign Initiatives
EU, Middle East, China, India likely view Nvidia-OpenAI concentration as a strategic dependency risk.
Reactions could include:
EU: Push for “sovereign compute” under the European Chips Act; fund Mistral or Graphcore.
Middle East (Saudi, UAE, Qatar): Double down on investing in alternative AI labs + AMD partnerships.
China: Strengthen domestic GPU efforts (Huawei Ascend, Biren chips) to counter US tech concentration.
Interactive AI Strategic Alliances & Competitive Landscape Map
Conclusion: A New Era of Ecosystem Strategy in AI
The partnership between Nvidia and OpenAI is a strategic realignment of the entire AI landscape. What we’re witnessing is not simply two companies joining forces, but the formation of a powerful new center of gravity.
This deal underscores a deeper truth: in AI, scale is strategy. Compute capacity, capital, data, and model development are all converging into tightly integrated stacks. Nvidia gains a long-term anchor customer and deeper control over the hardware layer; OpenAI gains unprecedented compute scale and greater independence from traditional cloud providers. Together, they’re setting a new benchmark for what “full-stack” AI development looks like.
But with this concentration of power come ripple effects. Competitors are already recalibrating — from Microsoft doubling down on vertical integration to Amazon and Google accelerating their own hardware strategies, and from Anthropic positioning itself as a safety-focused alternative to governments pushing for sovereign compute. Even chipmakers like AMD, Intel, and specialized startups see opportunities to form counter-alliances and differentiate themselves in this rapidly consolidating market.
The implications go far beyond market share. The way AI is built, deployed, and governed is being rewritten in real time. The stakes include not just who leads the next wave of AI innovation, but how power, access, and opportunity are distributed across the global technology landscape.
This is why understanding the ecosystem as a network — not just a collection of companies — is now essential. The AI Strategic Alliances & Competitive Landscape Map we’ve built is designed to help leaders see this shifting terrain clearly, explore potential alignments, and anticipate how today’s moves could shape tomorrow’s realities.
Author

Gianluca Caccamo connects Leaders with Data for Strategic Partnerships, after more than 15 years at companies like Google, Pinterest and Wix among others. Advising companies on E-commerce, Advertising, Saas and AI Partnerships. [Linkedin]
Follow us on Linkedin ❤️
Sources
The Verge – Nvidia is partnering up with OpenAI to offer compute and cash
The Guardian – Nvidia to invest $100bn in OpenAI, bringing the two AI firms together
Google Cloud Blog – Introducing Cloud TPU v5p and AI Hypercomputer
Google Cloud – TPU transformation: A look back at 10 years of AI chips
https://www.finance-monthly.com/nvidia-100b-openai-investment/?utm_source=chatgpt.com






Comments